-
-
-
siddharthshroff92@gmail.com
Anugrah Clinic, Hiranandani Meadows, Thane 400610.
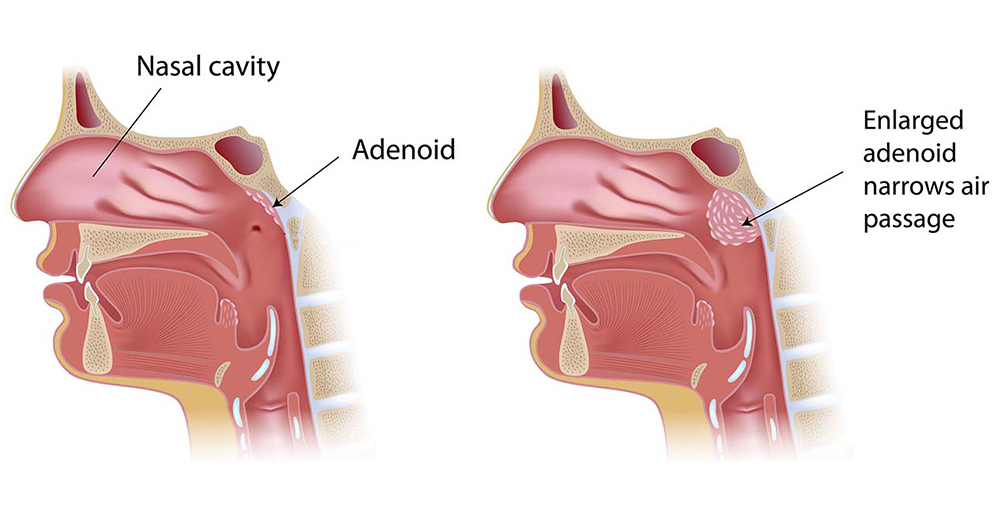
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, which are small lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal passage. Adenoids play a role in immune defense during early childhood, but they can become enlarged or chronically infected, leading to various health problems.
Enlargement or infection of the adenoids often occurs due to repeated upper respiratory tract infections, allergies, or chronic sinusitis. In some children, adenoids naturally grow large and may block the airway or eustachian tube, even without active infection.
These symptoms are more common in children, as adenoids tend to shrink naturally during adolescence.
Initial management may involve antibiotics for infection, nasal steroid sprays, or allergy control measures. However, if symptoms persist or cause significant breathing, sleeping, or ear problems, an adenoidectomy may be recommended.
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and often takes less than 30 minutes. It may be done alone or combined with a tonsillectomy or ear tube insertion, depending on the child’s condition. Recovery is generally quick, with most children resuming normal activities within a week.