-
-
-
siddharthshroff92@gmail.com
Anugrah Clinic, Hiranandani Meadows, Thane 400610.
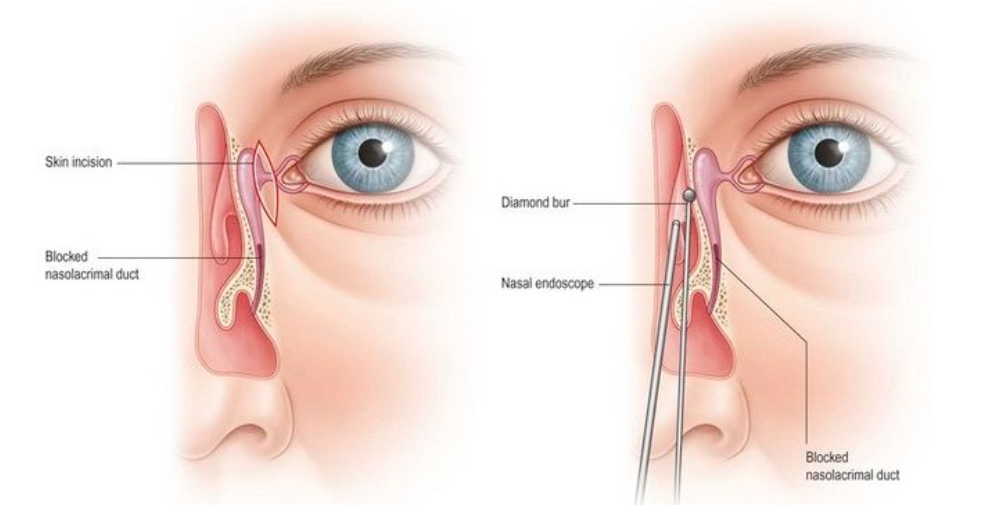
Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (Endoscopic DCR) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat nasolacrimal duct obstruction—a condition in which the tear drainage pathway between the eye and nose becomes blocked. This blockage leads to excessive tearing (epiphora), recurrent eye infections, and discomfort.
The obstruction can be congenital (present from birth) or acquired. Common acquired causes include chronic nasal or sinus infections, trauma to the nose, nasal polyps, inflammation from conditions like chronic dacryocystitis, and age-related narrowing of the tear duct. Rarely, tumors along the lacrimal drainage system or nasal cavity may cause blockage.
Typical symptoms include persistent watery eyes, recurrent eye infections, discharge from the inner corner of the eye, swelling near the side of the nose, and pain or tenderness over the lacrimal sac. In some cases, redness and pus discharge occur, especially during acute infection.
Endoscopic DCR is performed using a nasal endoscope, eliminating the need for an external skin incision. Under local or general anesthesia, the surgeon accesses the blocked tear duct through the nasal cavity, removes the bony obstruction, and creates a new passage between the lacrimal sac and nasal cavity to restore tear drainage. A small silicone stent may be inserted temporarily to keep the passage open during healing.
This technique offers several benefits—no external scar, faster recovery, less tissue damage, and preservation of normal anatomy. Postoperative care includes nasal irrigation, antibiotic or anti-inflammatory eye drops, and regular follow-up to ensure proper healing and stent removal if placed.