-
-
-
siddharthshroff92@gmail.com
Anugrah Clinic, Hiranandani Meadows, Thane 400610.
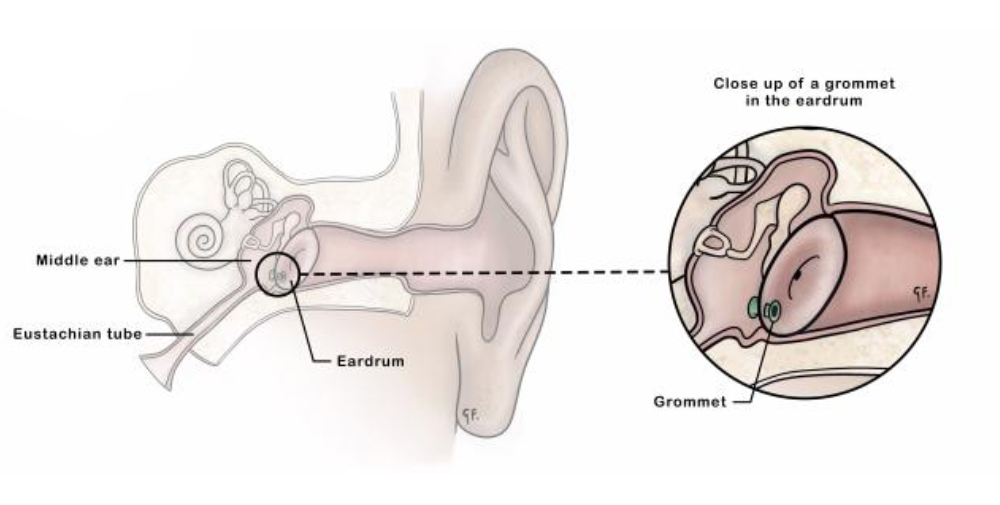
Grommet insertion, also known as tympanostomy tube insertion, is a common otology procedure performed to treat persistent middle ear problems, especially in children. A grommet is a small ventilation tube surgically placed into the eardrum (tympanic membrane) to allow air to enter the middle ear and fluid to drain out, thus restoring normal ear function.
Grommet insertion is mainly indicated for Otitis Media with Effusion (OME), where fluid accumulates in the middle ear without active infection. Common causes include recurrent middle ear infections, eustachian tube dysfunction, enlarged adenoids, allergies, or frequent upper respiratory tract infections. Persistent fluid can affect hearing and speech development in children.
Patients may experience hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in the ear, balance problems, irritability in children, and delayed speech or language development. Some may have recurrent ear infections, difficulty responding to sounds, or poor school performance due to hearing impairment.
When conservative treatments like antibiotics, nasal sprays, or observation fail to resolve fluid accumulation after several weeks or months, grommet insertion is recommended. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. A small incision is made in the eardrum (myringotomy), the fluid is suctioned out, and the grommet is inserted. The tube remains in place for 6–12 months, naturally falling out as the eardrum heals. Post-surgery, patients usually notice immediate hearing improvement. Water precautions may be advised to prevent infections.
Grommet insertion is a safe, quick, and effective procedure, helping prevent recurrent infections, improving hearing, and supporting speech and language development in children.