-
-
-
siddharthshroff92@gmail.com
Anugrah Clinic, Hiranandani Meadows, Thane 400610.
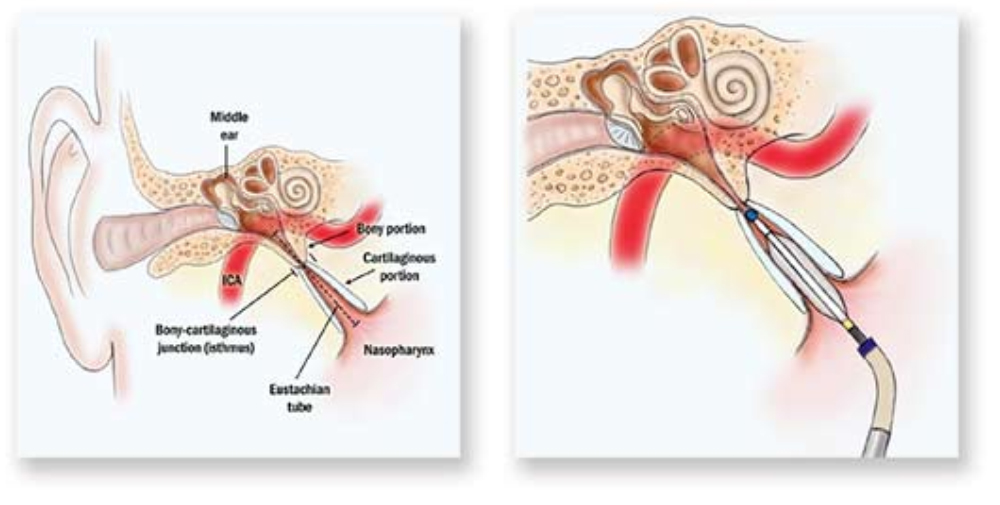
Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation (ETBD) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), a condition in which the Eustachian tubes fail to open and close properly. The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the nose, helping to equalize ear pressure and drain fluid.
ETD may result from chronic sinus infections, allergies, upper respiratory infections, nasal polyps, or structural blockages. Inflammation from colds or allergies can cause swelling, while conditions like adenoid enlargement or tumors may physically obstruct the tube. Smoking and frequent air travel or diving can also contribute.
Common symptoms include a feeling of fullness in the ear, muffled hearing, ear pain, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), popping or crackling sounds, and difficulty balancing. In severe cases, persistent ETD can lead to middle ear infections (otitis media) or fluid buildup (otitis media with effusion). Symptoms often worsen with altitude changes, such as during flights.
For persistent ETD unresponsive to medical therapy, ETBD offers an effective solution. During the procedure, a small balloon catheter is inserted through the nose into the Eustachian tube opening. The balloon is inflated for a short time to widen and remodel the tube, improving ventilation and drainage. The balloon is then deflated and removed. The procedure is usually performed under local or general anesthesia, is quick, and has a short recovery time.
ETBD has shown significant long-term benefits in reducing symptoms, improving hearing, and preventing recurrent ear infections, with minimal risk of complications.